提示 :此条目的主题不是
科学记数法 。
e
{\displaystyle e}
数学常数 ,是自然对数函数 的底数 ,亦称自然常数 、自然底数 ,或是欧拉数 (Euler's number ),以瑞士数学家欧拉 命名;还有个较少见的名字纳皮尔常数 ,用来纪念苏格兰 数学家约翰·纳皮尔 引进对数 。它是一个无限不循环小数,数值约是(小数点后20位,A001113
欧拉数 数表 —无理数
2
{\displaystyle \color {blue}{\sqrt {2}}}
φ
{\displaystyle \color {blue}\varphi }
3
{\displaystyle \color {blue}{\sqrt {3}}}
5
{\displaystyle \color {blue}{\sqrt {5}}}
δ
S
{\displaystyle \color {blue}\delta _{S}}
e
{\displaystyle \color {blue}e}
π
{\displaystyle \color {blue}\pi }
命名 数字 2.7182818284 名称 欧拉数纳皮尔常数 识别 种类 无理数 超越数 发现 雅各布·伯努利 符号
e
{\displaystyle e}
位数 数列编号 A001113 性质 定义
e
=
lim
n
→
∞
(
1
+
1
n
)
n
{\displaystyle e=\lim _{n\to \infty }\left(1+{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}}
e
=
lim
t
→
0
(
1
+
t
)
1
t
{\displaystyle e=\lim _{t\to 0}(1+t)^{\frac {1}{t}}}
以此为根 的多项式或函数
∫
1
x
d
t
t
=
1
{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{x}{\frac {\mathrm {d} t}{t}}=1}
表示方式 值 2.7182818284 无穷级数
∑
n
=
0
∞
1
n
!
{\displaystyle \sum \limits _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {1}{n!}}}
二进制 10.10110111 1110 0001 0101 0001 … [1] 八进制 2.55760521 3050 5355 1246 5277 … [2] 十进制 2.71828182 8459 0452 3536 0287 … 十二进制 2.87523606 9821 9BA7 1971 009B … [3] 十六进制 2.B7E15162 8AED 2A6A BF71 5880 … [4] 六十进制 2;43,5,48,52,29,48,35,6,46,19,55…
e
{\displaystyle e}
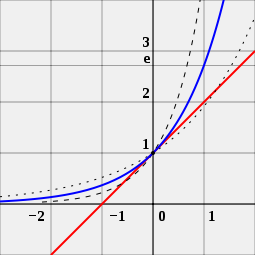
是使在
x
=
0
{\displaystyle x=0}
点上
f
(
x
)
=
a
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=a^{x}}
(蓝色曲线)的
导数(切线的 斜率 )值为1之
a
{\displaystyle a}
的唯一值。对比一下,函数
2
x
{\displaystyle 2^{x}}
(虚点曲线)和
4
x
{\displaystyle 4^{x}}
(虚线曲线)和斜率为1、
y -截距为1的直线(红色)并不相切。
e
=
2.71828182845904523536
⋯
{\displaystyle e=2.71828182845904523536\cdots }
271801
99990
{\displaystyle {\frac {271801}{99990}}}
历史
第一次提到常数
e
{\displaystyle e}
对数 著作附录中的一张表。但它没有记录这常数 ,只有由它为底计算出的一张自然对数列表,通常认为是由威廉·奥特雷德 制作。第一次把
e
{\displaystyle e}
雅各布·伯努利 ,他尝试计算下式的值:
lim
n
→
∞
(
1
+
1
n
)
n
{\displaystyle \lim _{n\to \infty }\left(1+{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}}
已知的第一次用到常数
e
{\displaystyle e}
莱布尼茨 于1690年和1691年给惠更斯 的通信,以
b
{\displaystyle b}
欧拉 开始用
e
{\displaystyle e}
e
{\displaystyle e}
Mechanica
c
{\displaystyle c}
e
{\displaystyle e}
用
e
{\displaystyle e}
e
{\displaystyle e}
exponential )一字的首字母。另一看法则称
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
{\displaystyle a,b,c,d}
e
{\displaystyle e}
定义
就像圆周率
π
{\displaystyle \pi }
虚数单位i ,
e
{\displaystyle e}
定义
e
{\displaystyle e}
极限 值:
e
=
lim
n
→
∞
(
1
+
1
n
)
n
{\displaystyle e=\lim _{n\to \infty }\left(1+{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}}
e
=
lim
t
→
0
(
1
+
t
)
1
t
{\displaystyle e=\lim _{t\to 0}(1+t)^{\frac {1}{t}}}
定义
e
{\displaystyle e}
阶乘倒数 之无穷级数 的和[5]
e
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
1
n
!
=
1
0
!
+
1
1
!
+
1
2
!
+
1
3
!
+
1
4
!
+
⋯
{\displaystyle e=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{1 \over n!}={1 \over 0!}+{1 \over 1!}+{1 \over 2!}+{1 \over 3!}+{1 \over 4!}+\cdots }
其中
n
!
{\displaystyle n!}
n
{\displaystyle n}
阶乘 。
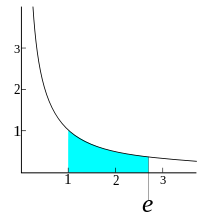
定义
e
{\displaystyle e}
x
{\displaystyle x}
∫
1
x
d
t
t
=
1
{\displaystyle \int _{1}^{x}{\frac {\mathrm {d} t}{t}}=1}
定义
e
{\displaystyle e}
x
{\displaystyle x}
lim
h
→
0
x
h
−
1
h
=
1
{\displaystyle \lim _{h\to 0}{\frac {x^{h}-1}{h}}=1}
这些定义可证明是等价的,请参见文章指数函数的特征描述
性质
x
x
{\displaystyle {\sqrt[{x}]{x}}}
的极大值在
x
=
e
{\displaystyle x=e}
.
很多增长或衰减过程都可以用指数函数模拟。指数函数
e
x
{\displaystyle e^{x}}
x
↦
k
e
x
{\displaystyle x\mapsto ke^{x}}
k
{\displaystyle k}
导数 相等。即:
d
d
x
e
x
=
e
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}e^{x}=e^{x}}
e
x
{\displaystyle e^{x}}
泰勒级数 为
e
x
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
x
n
n
!
∀
x
{\displaystyle e^{x}=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{n}}{n!}}\quad \forall x}
=
1
+
x
+
x
2
2
!
+
x
3
3
!
+
.
.
.
{\displaystyle =1+x+{\frac {x^{2}}{2!}}+{\frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+...}
x
{\displaystyle x}
sin
x
{\displaystyle \sin x}
cos
x
{\displaystyle \cos x}
欧拉公式 的重要等式:
e
i
x
=
cos
x
+
i
sin
x
{\displaystyle e^{\mathrm {i} x}=\cos x+{\rm {i}}\sin x}
当
x
=
π
{\displaystyle x=\pi }
欧拉恒等式 :
e
i
π
+
1
=
0
{\displaystyle e^{\mathrm {i} \pi }+1=0}
此式被理查德·费曼 称为“欧拉的宝石”。
(
cos
x
+
i
sin
x
)
n
=
(
e
i
x
)
n
=
e
i
n
x
=
cos
(
n
x
)
+
i
sin
(
n
x
)
{\displaystyle (\cos x+i\sin x)^{n}=\left(e^{ix}\right)^{n}=e^{inx}=\cos(nx)+i\sin(nx)}
即棣莫弗公式 。
e
{\displaystyle e}
无理数 和超越数 (见林德曼-魏尔斯特拉斯定理 )。这是第一个获证为超越数的数,而非故意构造的(比较刘维尔数 );由夏尔·埃尔米特 (Charles Hermite )于1873年证明。有猜想它为正规数 。当
x
=
e
{\displaystyle x=e}
f
(
x
)
=
x
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\sqrt[{x}]{x}}}
e
{\displaystyle e}
连分数 展开式有个有趣的模式,可以表示如下( A003417
e
=
[
2
;
1
,
2
,
1
,
1
,
4
,
1
,
1
,
6
,
1
,
1
,
8
,
1
,
1
,
10
,
1
,
1
,
12
,
…
]
{\displaystyle e=[2;1,2,1,1,4,1,1,6,1,1,8,1,1,10,1,1,12,\ldots ]}
就像以下的展开式:
e
=
2
+
1
1
+
1
2
+
1
1
+
1
1
+
1
4
+
1
1
+
1
1
+
1
6
+
1
1
+
⋱
{\displaystyle e=2+{\cfrac {1}{1+{\cfrac {1}{\mathbf {2} +{\cfrac {1}{1+{\cfrac {1}{1+{\cfrac {1}{\mathbf {4} +{\cfrac {1}{1+{\cfrac {1}{1+{\cfrac {1}{\mathbf {6} +{\cfrac {1}{1+\ddots }}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}
无理数证明
证明
e
{\displaystyle e}
反证法 。假设
e
{\displaystyle e}
有理数 ,则可以表示成
a
b
{\displaystyle {\frac {a}{b}}}
a
,
b
{\displaystyle a,b}
e
{\displaystyle e}
考虑数字
x
=
b
!
(
e
−
∑
i
=
0
b
1
i
!
)
{\displaystyle x=b!\left(e-\sum _{i=0}^{b}{1 \over i!}\right)}
以下将推导出
x
{\displaystyle x}
e
{\displaystyle e}
x
{\displaystyle x}
0
<
x
=
b
!
(
e
−
∑
i
=
0
b
1
i
!
)
=
b
!
(
a
b
−
∑
i
=
0
b
1
i
!
)
{\displaystyle 0<x=b!\left(e-\sum _{i=0}^{b}{1 \over i!}\right)=b!\left({a \over b}-\sum _{i=0}^{b}{1 \over i!}\right)}
=
a
(
b
−
1
)
!
−
∑
i
=
0
b
b
!
i
!
{\displaystyle =a(b-1)!-\sum _{i=0}^{b}{b! \over i!}}
=
a
(
b
−
1
)
!
−
[
1
+
∑
n
=
0
b
−
1
b
(
b
−
1
)
⋯
(
n
+
1
)
]
{\displaystyle =a(b-1)!-\left[1+\sum _{n=0}^{b-1}b(b-1)\cdots (n+1)\right]}
x
{\displaystyle x}
0
<
x
=
b
!
∑
n
=
b
+
1
∞
1
n
!
{\displaystyle 0<x=b!\sum _{n=b+1}^{\infty }{1 \over n!}}
=
1
b
+
1
+
1
(
b
+
1
)
(
b
+
2
)
+
1
(
b
+
1
)
(
b
+
2
)
(
b
+
3
)
+
⋯
{\displaystyle ={\frac {1}{b+1}}+{\frac {1}{(b+1)(b+2)}}+{\frac {1}{(b+1)(b+2)(b+3)}}+\cdots }
<
1
b
+
1
+
1
(
b
+
1
)
2
+
1
(
b
+
1
)
3
+
⋯
=
1
b
≤
1
{\displaystyle <{\frac {1}{b+1}}+{\frac {1}{(b+1)^{2}}}+{\frac {1}{(b+1)^{3}}}+\cdots ={1 \over b}\leq 1}
但是0与1之间(不含0与1)不存在有整数,故原先假设矛盾,得出
e
{\displaystyle e}
二项式定理 视
n
{\displaystyle n}
二项式定理 可证出:
e
=
lim
n
→
∞
(
1
+
1
n
)
n
{\displaystyle e=\lim _{n\to \infty }\left(1+{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}}
=
lim
n
→
∞
∑
i
=
0
n
C
i
n
1
n
−
i
(
1
n
)
i
{\displaystyle =\lim _{n\to \infty }\sum _{i=0}^{n}C_{i}^{n}1^{n-i}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{i}}
=
lim
n
→
∞
[
C
0
n
1
n
(
1
n
)
0
+
C
1
n
1
n
−
1
(
1
n
)
1
+
C
2
n
1
n
−
2
(
1
n
)
2
+
C
3
n
1
n
−
3
(
1
n
)
3
+
.
.
.
+
C
n
n
1
0
(
1
n
)
n
]
{\displaystyle =\lim _{n\to \infty }\left[C_{0}^{n}1^{n}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{0}+C_{1}^{n}1^{n-1}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{1}+C_{2}^{n}1^{n-2}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{2}+C_{3}^{n}1^{n-3}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{3}+...+C_{n}^{n}1^{0}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}\right]}
=
lim
n
→
∞
[
1
×
1
+
n
×
1
n
+
n
!
(
n
−
2
)
!
2
!
×
1
n
2
+
n
!
(
n
−
3
)
!
3
!
×
1
n
3
+
.
.
.
+
1
×
1
n
n
]
{\displaystyle =\lim _{n\to \infty }\left[1\times 1+n\times {\frac {1}{n}}+{\frac {n!}{\left(n-2\right)!2!}}\times {\frac {1}{n^{2}}}+{\frac {n!}{\left(n-3\right)!3!}}\times {\frac {1}{n^{3}}}+...+1\times {\frac {1}{n^{n}}}\right]}
=
lim
n
→
∞
[
1
+
1
+
n
×
(
n
−
1
)
2
n
2
+
n
×
(
n
−
1
)
(
n
−
2
)
3
×
2
n
3
+
.
.
.
+
1
n
n
]
{\displaystyle =\lim _{n\to \infty }\left[1+1+{\frac {n\times \left(n-1\right)}{2n^{2}}}+{\frac {n\times \left(n-1\right)\left(n-2\right)}{3\times 2n^{3}}}+...+{\frac {1}{n^{n}}}\right]}
=
2
+
1
2
+
1
6
+
.
.
.
{\displaystyle =2+{\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{6}}+...}
=
2.71828...
{\displaystyle =2.71828...}
已知位数
e
{\displaystyle e}
[6] [7] 日期
位数
计算者
1748年
18
李昂哈德·欧拉
1853年
137
William Shanks
1871年
205
William Shanks
1884年
346
J. M. Boorman
1946年
808
?
1949年
2,010
约翰·冯·诺伊曼
1961年
100,265
Daniel Shanks & 约翰·威廉·伦奇
1978年
116,000
史蒂芬·盖瑞·沃兹尼克
1994年
10,000,000
Robert Nemiroff & Jerry Bonnell
1997年5月
18,199,978
Patrick Demichel
1997年8月
20,000,000
Birger Seifert
1997年9月
50,000,817
Patrick Demichel
1999年2月
200,000,579
Sebastian Wedeniwski
1999年10月
869,894,101
Sebastian Wedeniwski
1999年11月21日
1,250,000,000
Xavier Gourdon
2000年7月10日
2,147,483,648
近藤茂、Xavier Gourdon
2000年7月16日
3,221,225,472
Colin Martin、Xavier Gourdon
2000年8月2日
6,442,450,944
近藤茂、Xavier Gourdon
2000年8月16日
12,884,901,000
近藤茂、Xavier Gourdon
2003年8月21日
25,100,000,000
近藤茂、Xavier Gourdon
2003年9月18日
50,100,000,000
近藤茂、Xavier Gourdon
2007年4月27日
100,000,000,000
近藤茂、Steve Pagliarulo
2009年5月6日
200,000,000,000
近藤茂、Steve Pagliarulo
2010年2月21日
500,000,000,000
余智恒(Alexander J. Yee)
2010年7月5日
1,000,000,000,000
近藤茂、余智恒(Alexander J. Yee)
2014年11月15日
1,048,576,000,000
David Galilei Natale
谐取
在Google 2004年的首次公开募股 ,集资额不是通常的整头数,而是$2,718,281,828,这当然是取最接近整数的
e
{\displaystyle e}
美元 。Google2005年的一次公开募股中,集资额是$14,159,265,与圆周率 有关。
Google 也是首先在硅谷 心脏地带,接着在马萨诸塞州剑桥 出现的神秘广告版 的幕后黑手,它写着{first 10-digit prime found in consecutive digits of e }.com(在
e
{\displaystyle e}
e
{\displaystyle e}
著名计算机科学家 高德纳 的软件Metafont 的版本号码趋向
e
{\displaystyle e}
TeX 的版本号是趋向于圆周率 的。 参见 参考文献
^ Sloane, N.J.A. (编). Sequence A004593 (Expansion of e in base 2) . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences . OEIS Foundation. ^ Sloane, N.J.A. (编). Sequence A004599 (Expansion of e in base 8) . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences . OEIS Foundation. ^ Sloane, N.J.A. (编). Sequence A027606 (e in duodecimal) . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences . OEIS Foundation. ^ Sloane, N.J.A. (编). Sequence A170873 (Hexadecimal expansion of e) . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences . OEIS Foundation. ^ Iwanami Sūgaku Jiten Fourth, Tokyo: Iwanami Shoten, 2007, ISBN 978-4-00-080309-0MR 2383190 (日语) ^ Sebah, P. and Gourdon, X.; The constant e and its computation (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 )
^ Gourdon, X.; Reported large computations with PiFast (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 )
![]() A001113):
A001113):




















![\mathbb{Z}[i]](/media/math_img/2072/9ffa94e9e2e6d9e5e5373d5fafb954b902743fde.svg)




![{\displaystyle \mathbb {Z} [\omega ]}](/media/math_img/2072/7ae955a9a0d0f342fc73aaafe28af604d23267f7.svg)